Press Brake Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide
I. Introduction
The maintenance of the press brake helps to prolong the service life and reduce the cost. The maintenance of the press brake is mainly divided into several parts, including the hydraulic system, mechanical parts, lubrication, electrical equipment, and tooling.
Daily maintenance of the press brake is trivial but relatively simple. Once the daily overview procedures are done, it's time to tackle specific maintenance tasks. Let's watch a specific press brake maintenance operation video together, and I hope it will be helpful to you.
II. Importance of Regular Maintenance Work
The importance of regular maintenance cannot be overstated. As we all know, the press brake's service life depends on the product's quality, but it also depends on the user's maintenance measures. Regular maintenance is not only necessary to prolong the service life of the press brake, but it can also eliminate faults and reduce the workpiece damage rate, decrease the the risk of contaminants entering the system, improve machine precision, as well as the potential danger to machinery operators.
A detailed periodic maintenance plan should be developed and documented in a form. Both press brake operators and maintenance personnel need a professional training. Regular maintenance can detect faults in the press brake in time and avoid expensive maintenance costs. This article will introduce several important aspects of press brake maintenance.
III. Overall Inspection
Before using the press brake, check the machine's overall condition. Check for any residues on the tooling areas and workbench. Check the condition of the upper and bottom die for defects and cracks. If the dies have cracks, they can affect the bending quality of the workpieces.
Test the accuracy of the back gauge and the stop finger's position. Also, test whether all buttons, switches, indicator lights and foot controls are sensitive. These can be routine inspection items before each press brakes use. Additionally, some important parts require special maintenance.
1. Hydraulic Circuit
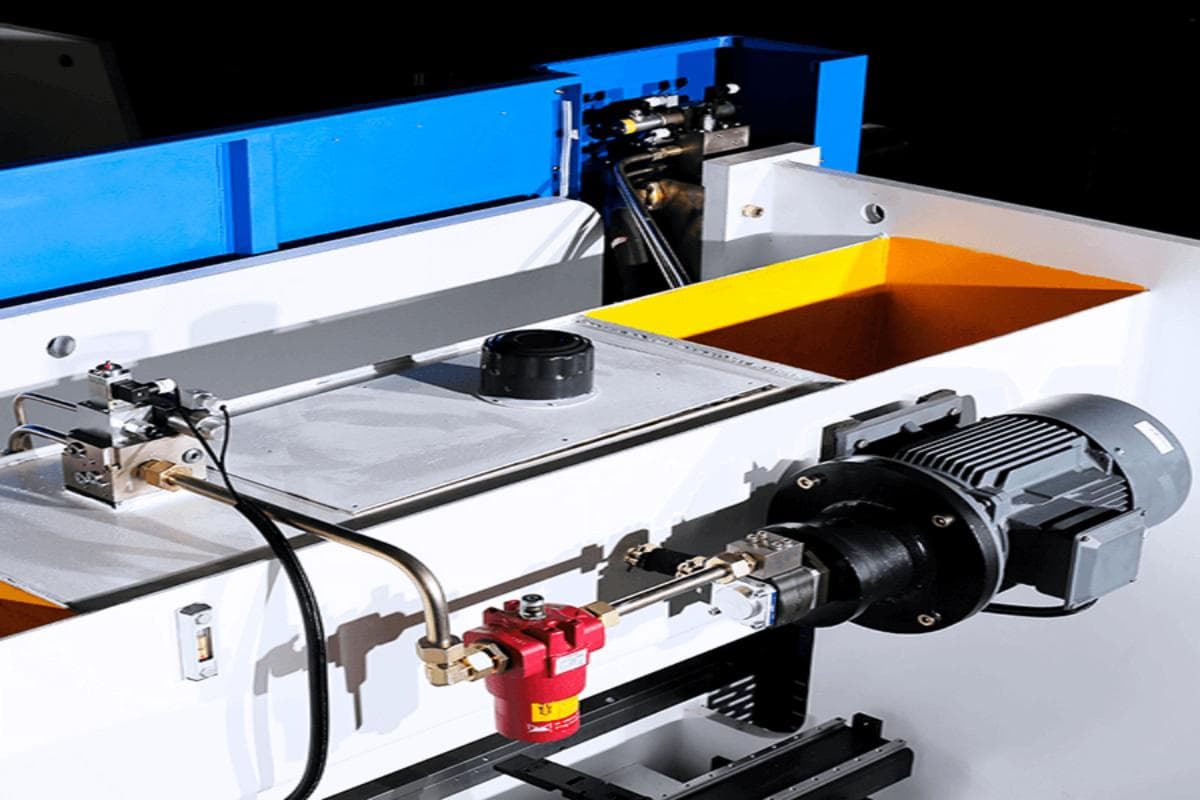
Hydraulic oil is the energy source of the hydraulic system. It is important to keep the oil and hydraulic circuits clean. The hydraulic circuit includes the oil tank, valve group, pipeline, motor, oil pump, etc. It is not recommended to use detergents when cleaning valves, oil tank covers, and related accessories.
Also, visually check whether the oil level in the oil tank is within the safe range every day. Otherwise, the operation of the hydraulic pump will be affected, resulting in insufficient power to drive the ram. Make sure that the oil tank is properly sealed and ventilated.
However, the oil tank cannot be completely sealed, and breathers are required to prevent the oil tank from generating a vacuum. The seal is designed to prevent particles from entering the tank and contaminating the oil. The contaminated oil can block the valve and damage the hydraulic pump, thus affecting the operation of the hydraulic system.
(1) Hydraulic fittings
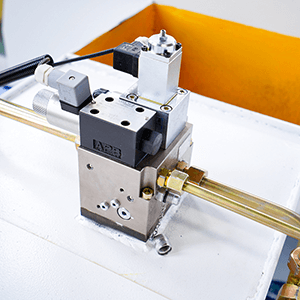
Check all pipes and hoses for leaks, especially the hydraulic pump and connecting accessories. In case of expansion of oil hoses, aging, or wear of pipelines, they should be replaced promptly. Check the cylinder assembly, valves, and hydraulic block for leaks.
Hydraulic press brakes have added maintenance requirements for parts like pistons and pumps. If there is too much oil on the piston, wipe it clean and apply proper lubrication. Check the maximum pressure of the pump and relief valve.
(2) Clean the oil tank and filters
Before replenishing the oil, it is necessary to clean the oil tank and filter. The filters of the oil inlet and outlet holes of the oil pump should be cleaned, and the air breathers on the oil tank need to be cleaned with compressed air.
The filter and air breathers may need to be replaced after a certain service life.
The oil temperature should not exceed 60 degrees as it can affect the stability of the oil and damage the accessories.
(3) The cleanness and level of the oil
Use the oil type recommended by the manufacturers to ensure the cleanliness of the oil. Check the oil level in the oil tank every day and use an electric pump to fill the oil.
The quality and viscosity of the oil should be checked every 4000 to 6000 hours of operation.
2. Mechanical Components
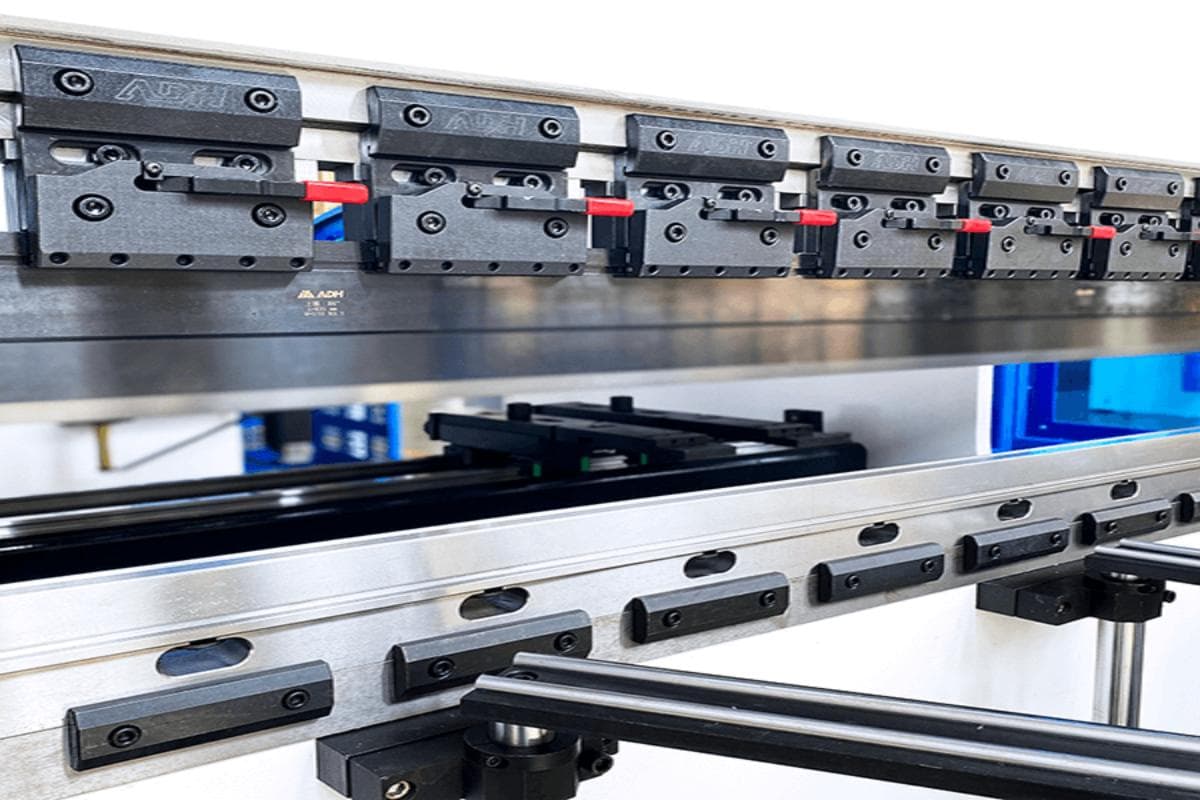

Regular inspection of the mechanical components is necessary to ensure the stability of all parts. It's important to tighten all bolts, nuts, and screws regularly and check the connection between the piston and the ram.
Inspect the base's connecting part for any cracks and examine the back gauge and stop finger's condition. Recalibration is necessary if required.
3. Lubrication System
The lubrication of press brake parts is an important factor in prolonging the machine's service life. Some parts of the press brake are subject to sliding, rolling, or friction. Lubrication can reduce friction and damage to components.
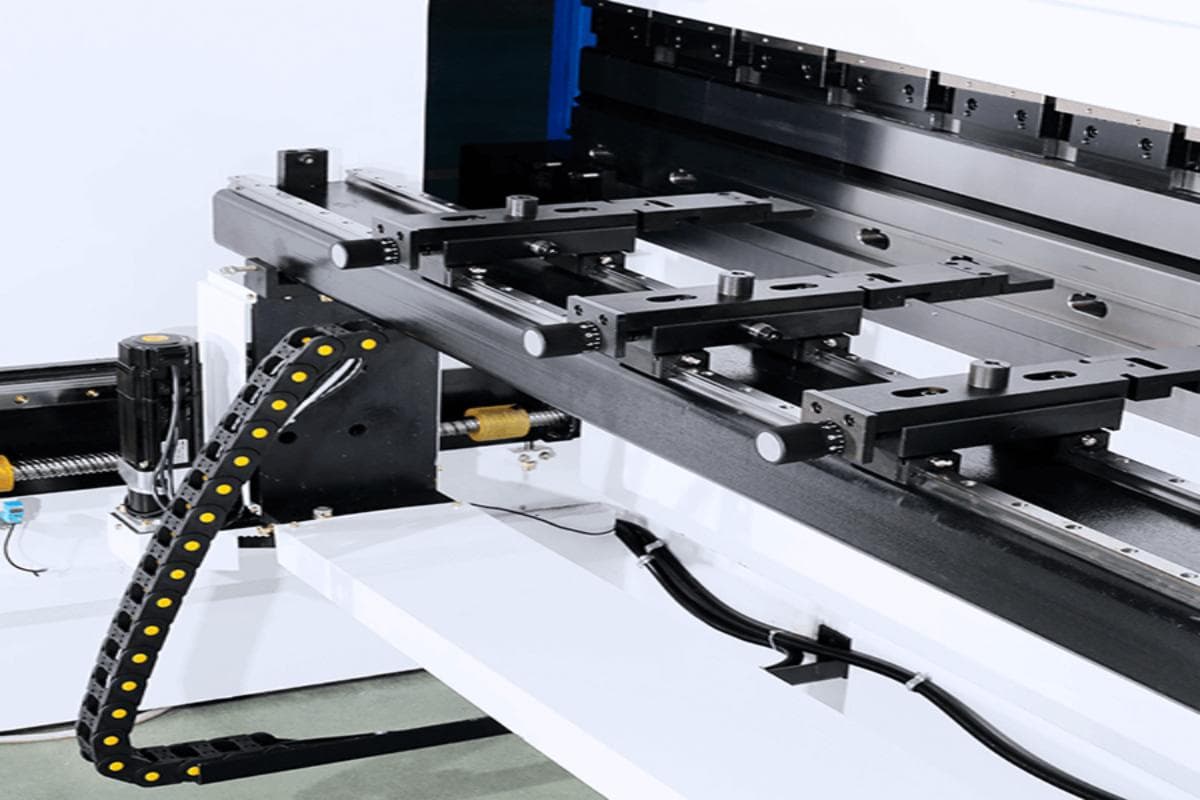
Parts requiring regular lubrication and cleaning include the ball screw, guide rail, back gauge, gear, etc. These should be lubricated at least once a week, and some parts may even need to be lubricated every day. Other parts, like the guides of the mobile beam, require yearly lubrication.
However, it's important not to over-lubricate, as this can cause insufficient friction or component contamination. Before applying lubricant or grease, make sure to clean all components and use the lubricating products recommended by the manufacturer.
4. Electrical Equipment
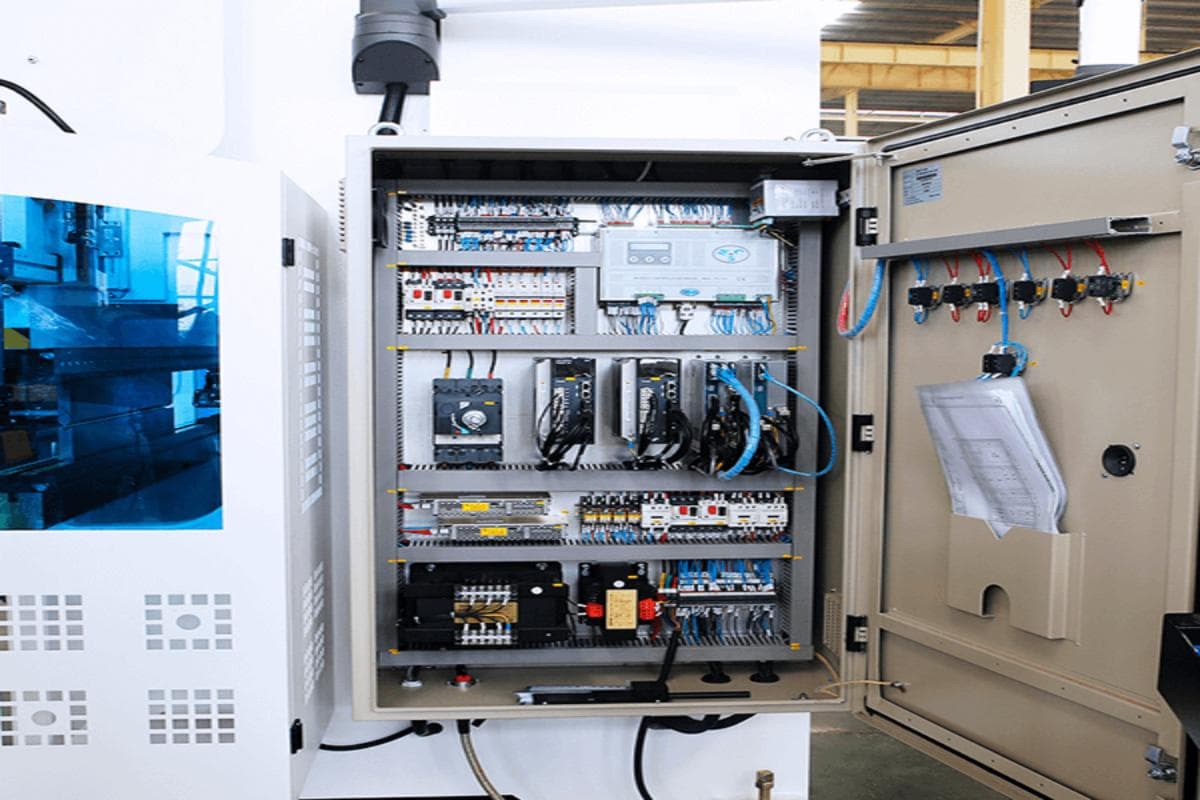

The maintenance of electrical equipment is a top priority to prolong the service life of the press brake. Check the entire electrical system at least once a year, including all electrical connections and switches.
Before the inspection, it is necessary to turn off the main power switch. Other inspections can be carried out after the power is on. Keep the components in a clean and safe condition when assembling electrical components.
Check the connection status of the terminal boxes and terminal strips on the monitor and relay. Check whether all wires are loose, whether insulation is damaged, and whether the wires are clean and orderly. If the wires are loose, tighten them and clean them with a clean cloth or compressed air.
Check the air filter of the electrical cabinet and inverter box and clean it with compressed air. Check all cables, printed circuit boards, and switches. If there is damage or a fault, repair and replace them. Check whether the limit switches and voltage are in good condition.
Keep the cooling fan and heat exchanger filter clean and in normal operation. Check whether the external electrical panel of the electrical box is turned off and whether the switches, lights, and other functions work normally.
5. Tooling System
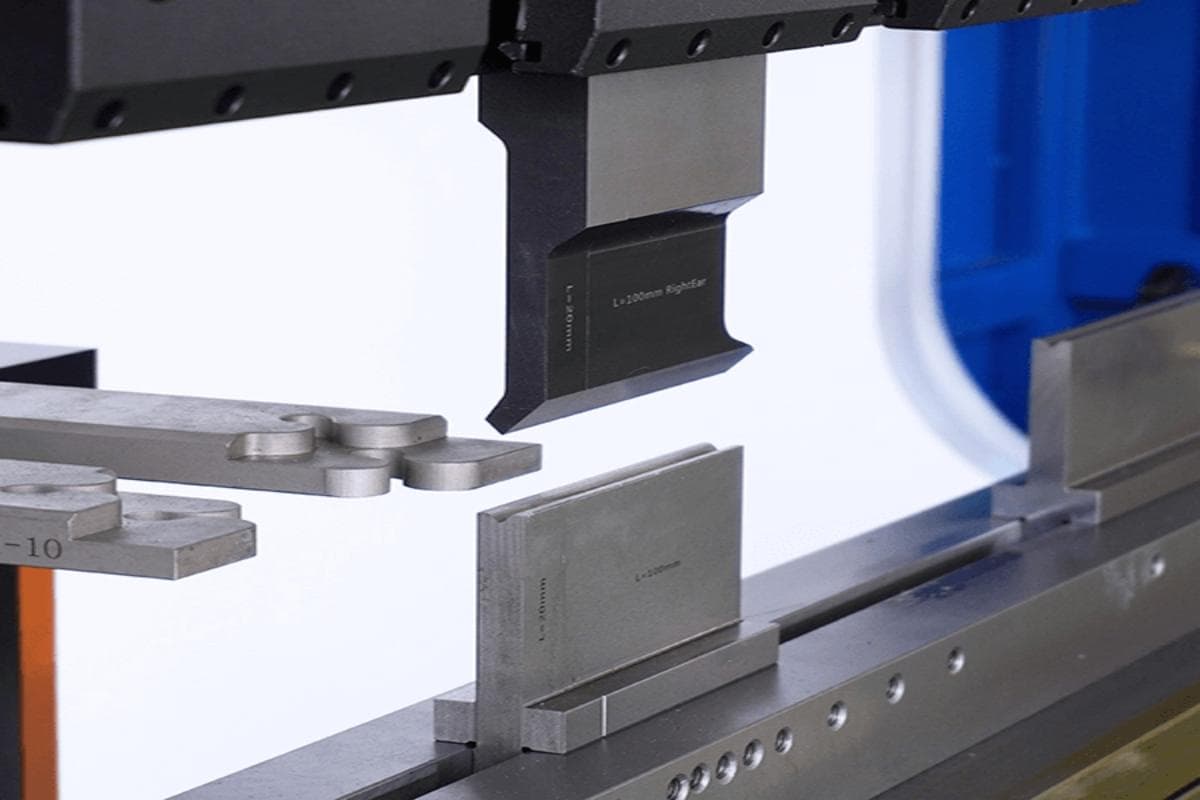
A press brake is a machine used to bend different sheet metals. Dust and dirt are the enemies of your whole machine, especially your tooling. It is essential to keep your press brake wiped down and clean. The punch and die of the machine will directly contact the plate, so the material of the die is particularly important. The material of the workpiece also needs to be considered, for the material with rolling chips will wear the die.
After use, the punch and die need to be maintained regularly to avoid rust and corrosion. After each use, wipe the punches and dies with a clean, lint-free towel and alcohol. Press brake tooling should not only be cleaned when it is changed, but it should be cleaned between each job, even if it is being left in the machine. Keep tooling clean and free from mill scale, and perform a visual inspection of tooling every time before use. This is done to eliminate fingerprints as the pH of the hands will corrode the die surface.
Then wear gloves to apply anti-corrosion lubricant to the punches and dies. Finally, put them into the toolbox and place at least one bag of silica gel in it. If the punch or die is damaged, it needs to be replaced.
IV. Important Precautions For Press Brake Maintenance
Cleaning the machine and carrying out scheduled maintenance is easy, but also requires special care and attention. Here are the potential hazards and corresponding safety precautions for each step in the press brake maintenance process:
1. Inspect and Clean the Machine
Potential Hazards:
- Mechanical Injury: Hands may get caught between moving parts of the machine during cleaning and inspection.
- Electric Shock: Exposed wires or damaged electrical components may cause electric shock.
Safety Measures:
- Mechanical Injury: Ensure the machine is completely powered off and the power source is locked out before cleaning and inspection. Use appropriate tools and methods to avoid direct contact with moving parts.
- Electric Shock: Check the integrity of wires and electrical components to ensure there are no exposed wires or damaged parts. Wear insulated gloves and other appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
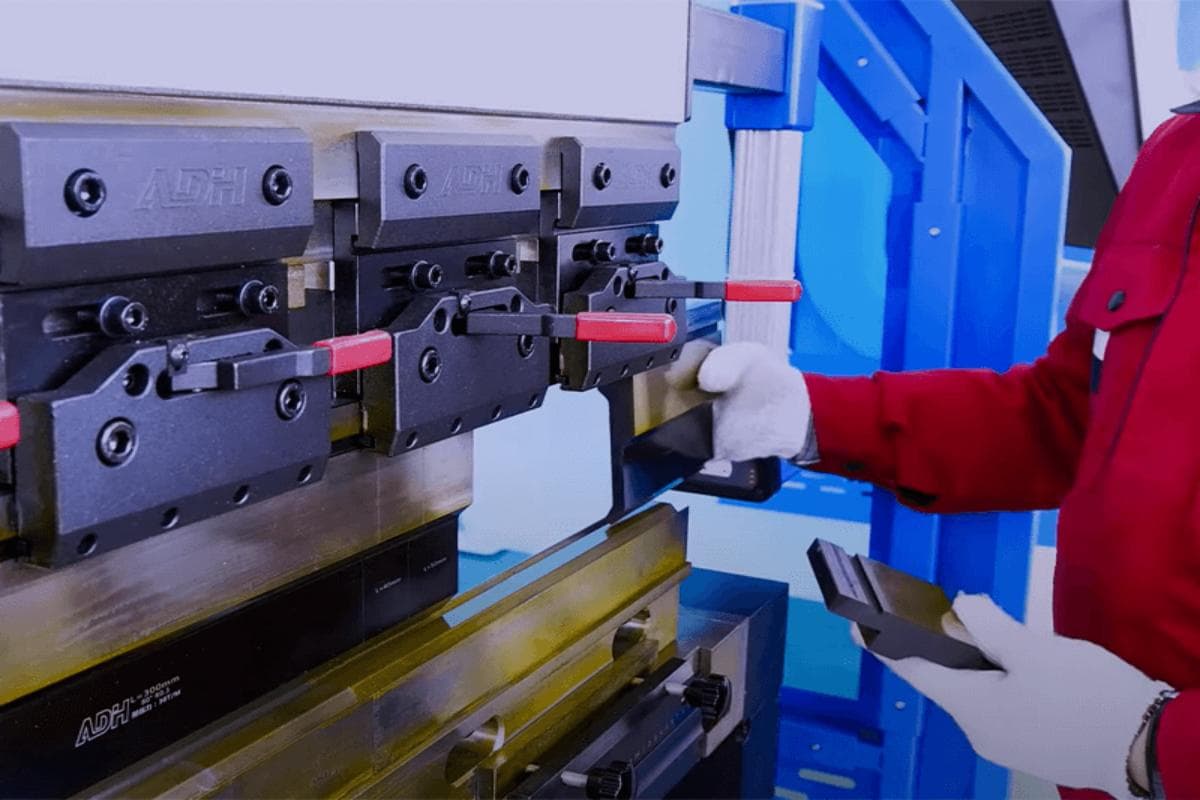

2. Lubricate the Machine
Potential Hazards:
- Slips and Falls: Spilled lubricant can make the floor slippery.
- Contact with Harmful Substances: Lubricants may be irritating to the skin and eyes.
Safety Measures:
- Slips and Falls: Use anti-slip mats during lubrication and ensure the floor is clean and dry. Immediately clean up any spilled lubricant.
- Contact with Harmful Substances: Wear protective gloves and goggles to avoid direct contact with lubricants.
3. Change the Dies
Potential Hazards:
- Pinching and Crushing: Hands may get caught between the dies and the machine during die changes.
- Heavy Object Injury: Dies are usually heavy and can cause muscle strain or other injuries during handling.
Safety Measures:
- Pinching and Crushing: Ensure the machine is completely powered off and the power source is locked out before changing dies. Use appropriate tools and methods to avoid direct contact with the clamping areas of the dies and the machine.
- Heavy Object Injury: Use mechanical lifting devices (such as cranes or hoists) to handle dies, avoiding manual lifting of heavy objects. Wear appropriate protective gloves and footwear.

4. Adjust Machine Settings
Potential Hazards:
- Mechanical Injury: Hands may get caught between moving parts of the machine during adjustments.
- Misoperation: Incorrect settings may cause machine malfunction or accidental startup.
Safety Measures:
- Mechanical Injury: Ensure the machine is completely powered off and the power source is locked out before making adjustments. Use appropriate tools and methods to avoid direct contact with moving parts.
- Misoperation: Carefully read the machine's operation manual before making adjustments to ensure correct operation. Perform a no-load test after adjustments to ensure settings are correct.
5. Perform Testing and Calibration
Potential Hazards:
- Mechanical Injury: Hands may get caught between moving parts of the machine during testing and calibration.
- Misoperation: Incorrect calibration may cause machine malfunction or accidental startup.
Safety Measures:
- Mechanical Injury: Ensure the machine is completely powered off and the power source is locked out before testing and calibration. Use appropriate tools and methods to avoid direct contact with moving parts.
- Misoperation: Carefully read the operation of press brake manual before performing testing and calibration to ensure correct operation. Perform a no-load test after calibration to ensure settings are correct.
V. Periodic Maintenance Plan
| Maintenance Schedule | Tasks |
| Daily | 1. Check hydraulic fluid levels and inspect for leaks 2. Inspect electrical components for loose connections or damage 3. Inspect dies for defects and cracks, and check alignment 4. Clean machine components, especially the hydraulic system 5. Check condition and alignment of punches and dies |
| Weekly | 1. Clean the machine to remove accumulated dust or debris 2. Clean and replace filters if necessary 3. Lubricate all moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer 4. Conduct a detailed assessment of the machine's overall condition 5. Check and adjust the alignment of the back gauge and ram |
| Monthly | 1. Examine the hydraulic system for signs of wear on seals and cylinders 2. Check for leaks and ensure proper pressure and flow 3. Check electrical components for loose connections or signs of overheating 4. Ensure proper grounding to avoid electrical hazards 5. Inspect frame, ram, bed, and back gauge system for wear, misalignment, or damage 6. Perform a thorough inspection of the machine's overall condition 7. Check condition of punches and dies, clean and lubricate tooling |
| Biannual | 1. Change hydraulic fluid and filters as recommended by the manufacturer 2. Perform a thorough inspection of the hydraulic system 3. Review and update control system software if updates are available 4. Conduct a comprehensive inspection of all electrical components and connections 5. Perform in-depth maintenance tasks, such as calibrating the machine and performing alignments 6. Inspect and maintain guide rails, back gauges, axes, and ball screws 7. Ensure all tooling is in good condition and properly aligned 8. Replace any worn or damaged punches and dies promptly |
| Annual | 1. Conduct a thorough inspection of the machine's overall condition 2. Test the accuracy of the back gauge and the stop finger's position 3. Perform a comprehensive inspection and servicing of the hydraulic system 4. Conduct a detailed inspection of all electrical components and connections 5. Perform a thorough inspection and maintenance of all mechanical components 6. Conduct a comprehensive inspection and maintenance of all tooling |

VI. Conclusion
Regular maintenance of the press brake is an effective way to prolong the machine's service life. Maintenance of the press brake includes the hydraulic circuit, hydraulic accessories, tooling system, and electronic accessories. Additionally, lubrication of mechanical parts, guide rails, back gauges, axes, ball screws, and other parts is necessary, as well as the cleaning of the foundation.
In addition to keeping the press brake machine clean, it is also important to clean the work area. A clean work area will reduce the frequency of cleaning the machine. Even though your operator and shop staff may be knowledgeable, it is a good idea to keep a trusted service technician or company on speed dial for those issues that aren’t easily resolved.
ADH is a professional manufacturer of a wide range of machine tools in metal sheet fabrication, like press brakes (CNC press brakes, NC press brakes, hydraulics, etc.), laser, and shearing. We also provide professional after-sales service. If you have any issues with your press brake, you can contact our after-sales team.
Screw Locking Milling Cutter
Screw Locking Milling Cutter,Emr Screw Locking Milling Cutter,Trs Screw Locking Milling Cutter,Exn03R Screw Locking Milling Cutter
SICHUAN JOJO TOOLS CO., LTD , https://www.jojo-tools.com