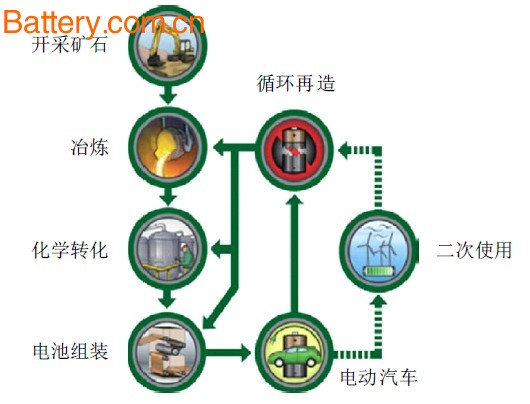
China's new energy vehicle policy is generally divided into several stages in terms of development. For example, from 2001 to 2007, it was the initial stage. This stage was mainly started with the 863 plan and was identified as “three verticals†(pure electric vehicles , hybrids). Automobiles, fuel cell vehicles ) and the "three horizontal" (power battery, drive motor, powertrain) research and development layout, and the introduction of the "new energy vehicle production access management rules." From 2008 to 2011, it was the promotion stage, such as the “Ten Cities and Thousands of Vehicles Projectâ€, and the state listed new energy vehicles in strategic emerging industries. Since 2012, it has officially entered the development stage, and new energy vehicle industry policies have been continuously introduced, including access management, financial subsidy policies, tax incentives, and infrastructure. It seems that the increasingly perfect Chinese new energy vehicle policy system, especially the subsidy policy, is a bit vulnerable to the exposure of the fraudulent incident. To some extent, the solution is the lag of policy introduction. In terms of subsidy policy, the cycle is long and the delivery may not be timely. Coupled with the impact of local protection, the development of new energy vehicles is limited. After the introduction of the new energy vehicle industry points management and the average fuel consumption management of passenger car companies, it will make up for the subsidy policy and some loopholes. Although there are a series of new energy vehicle support policies, new energy vehicles still need to solve many of the difficulties they are facing, such as the lack of real core technology and inadequate infrastructure planning. Therefore, the new energy automobile industry has a long way to go before it is truly market-oriented. There are many suggestions and opinions on how to implement the new energy vehicle policy, mostly from a macro or overall level. In fact, it should be specific to the specific details, this article on the power battery recycling policy to talk about their own views. The author has conducted some discussions on the recycling technology and process of power batteries. At that time, it was mentioned that in the field of recycling of used power batteries, China only has the "Solid Waste Pollution Prevention and Control Law" and the "Circular Economy Promotion Law" and the recycling of used power batteries. At present, the new policy of “Electric Vehicle Power Battery Recycling Technology Policy (2015 Edition)†has been issued, which can be regarded as a treatment plan for the future life of the power battery. Despite the introduction of this policy, there is still a lack of comprehensive and specific professional laws and regulations on the recycling of used power batteries, and the technical standards are relatively backward. According to the China Automotive Technology and Research Center, by 2020, the cumulative scrap of power batteries for pure electric (including plug-in) passenger cars and hybrid passenger cars in China will reach 12 to 170,000 tons. How to recycle and dispose of these used batteries, and to remove short-term ladders, have not seen a better solution. Similar to the problems faced by recycling used cars: (1) The recycling rate of scrapped cars is low, and most of the scrapped cars flow to the second-hand market. However, if the power battery cannot be standardized for recycling after the end of its service life, it will also cause harm to unknown use. (2) The overall level of scrapped car recycling and dismantling enterprises is low, the scale is small and the dismantling technology is backward. Unregulated operation and stacking will cause environmental pollution. If the recycling of the power battery is not handled, the pollution problem is more serious. (3) At present, the tax rate of foreign automobile dismantling enterprises is about 3%-5%, and the taxes and fees paid by China's scrap car recycling and dismantling enterprises are as high as 20% or more, and most enterprises cannot afford them for a long time. In the absence of an economic compensation policy, companies engaged in related recycling and utilization are not supported, and the difficulty in making profits makes the late investment insufficient to fall into a situation of abandonment. Therefore, in addition to the limitations of technical conditions, the lack of access conditions and management systems for recycling enterprises are also restricting the effective recycling of power batteries. It is necessary to learn from foreign related experience to establish a complete recycling system for used power batteries. It is also suggested that the state should not only have incentives and guiding policies at the policy level, but also punitive measures. As long as it is engaged in the power battery recycling industry chain, whether it is a power battery manufacturer or an OEM or a recycling company, it will be punished if it fails to achieve the planned goals. In order to avoid the occurrence of things that do not hang high, this is irresponsible for the development of new energy vehicles. There will be overcapacity in the boom of the new energy auto industry. If the extensive development model is adopted, the recovery of power batteries will be more difficult. The fundamental purpose of strengthening the recycling and reuse of power batteries is to truly realize the sustainable development of new energy vehicles. Efficient and reasonable recovery and utilization of power batteries can not wait until the new energy vehicle market develops before considering and planning, repeating the mistakes of some previous policies and loopholes. It should be just now, right now, the government and enterprises, policies and technology, multi-pronged, to provide better support for the further development of new energy auto companies in the future. Portable Potato Grinder,Electric Potato Masher,Oxo Potato Masher,Mash Potato Masher Hunan Xinta Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. , https://www.xyagriculture.com